
TeleClinical Care (TCC)
.png)
1. Overview
Project Overview
The TeleClinical Care (TCC) mental health module was designed to transform outdated paper-based mental health assessments into an efficient, user-friendly digital solution. This module streamlined processes for both patients and clinicians, addressing critical gaps in accessibility, accuracy, and real-time feedback. Over the course of a year, I led the end-to-end design and development of this module, working closely with healthcare professionals and leveraging research-driven insights to create a tool that bridges the gap between technology and mental healthcare.
01
Role
UX Designer & Front-End Developer
04
Team
Collaborative effort with clinicians and a supervising professor
02
Project Type
Mobile App Design – Thesis Project
05
Date
September 2020 - August 2021 (1 Year)
03
Location
Sydney, Australia
06
Tools Used
Adobe XD (design),
React Native(development),
Redux (state management), JIRA (agile management)
Problem Statement
Mental health disorders impact nearly half of Australians aged 16 to 85. Unfortunately, the assessment process often involves outdated pen-and-paper questionnaires that are time-consuming, error-prone, and inaccessible to many patients.
Key Problem:
How might we create a digital tool that simplifies mental health assessments, ensuring it’s accessible, accurate, and easy to use for both patients and clinicians?
2. Research & Insights
This project began with a solid foundation of research. Understanding the complexities of mental health assessments and their impact on both clinicians and patients was key to designing a solution that could truly make a difference.
Here's how I approached it step by step:
.png)
Step 1: Literature Review
To start, I dove deep into academic research to understand the fundamentals.
To design an effective and accessible mental health module, I explored the clinical utility of questionnaires and the impact of transitioning from paper-based to electronic delivery. This research provided critical insights into how digital tools can transform mental health care.
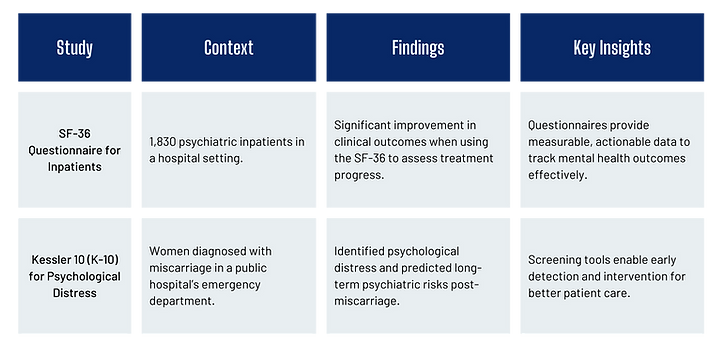
Literature Review 1. Questionnaires in Mental Health Treatment
The following studies demonstrate the clinical effectiveness of questionnaires in mental health care:
.png)
Key Takeaway: These studies highlight the power of questionnaires in providing accurate, actionable insights that support both patients and clinicians.
Literature Review 2. Questionnaires in Mental Health Treatment
The following studies demonstrate the clinical effectiveness of questionnaires in mental health care:

Key Takeaway: Transitioning to digital questionnaires enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and enables real-time feedback, transforming how mental health data is collected and utilized.
How this shaped the TCC - Mental health Module
These findings informed the design of the TeleClinical Care module by emphasizing:
.png)
With the literature review setting the stage, I next focused on implementing research-backed design philosophies. These principles, derived from established frameworks and studies, guided the creation of user-friendly, clinically reliable questionnaires for the TeleClinical Care module.
Step 2: Questionnaire - Design Philosophies
The foundation for designing the TeleClinical Care questionnaires was rooted in research-backed principles. These were drawn from the Framework of Questionnaire Design, which combines general principles (focused on user experience and survey objectives) and specific principles (focused on the structure, layout, and format of the questions).
By synthesizing these sources, I adopted the following five design philosophies to ensure the questionnaires were both effective and user-centered:

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
By applying these five research-driven design philosophies, the TeleClinical Care questionnaires achieved a balance of scientific rigor and user accessibility. These principles ensured that the tools were not only effective for clinicians but also approachable and engaging for users.
With the design philosophies guiding the structure of the questionnaires, I turned my attention to understanding the competitive landscape. Evaluating existing mental health apps helped me identify key gaps and opportunities to ensure the TeleClinical Care module addressed unmet needs while providing unique value to both patients and clinicians.
Step 3: Competitive Analysis
To ensure the TeleClinical Care module was both innovative and effective, I explored leading mental health apps: Moodfit, Mentemia, MoodMission, and Sanvello. This analysis revealed their strengths and weaknesses, allowing me to identify critical gaps that TeleClinical Care could fill to stand out in the market.
.png)
What Competitors Do Well
Moodfit: Offers a clean, intuitive interface for goal tracking and mood insights, making it approachable for users.
Mentemia: Uses gamified elements to engage users and promote mental health habits.
Sanvello: Provides a sleek, modern design with tools for self-care and guided meditations
Gaps That TeleClinical Care Addresses
Emergency Support Integration: None of the competitors provide immediate access to crisis resources, a critical feature for users at risk.
Real-Time Feedback: All the apps lack real-time scoring or actionable insights, leaving users without a clear understanding of their results.
Clinician Support: Competitors focus solely on self-help, without offering tools for clinicians to visualize or export patient data.
TeleClinical Care's Mental Health Module bridges the gap between self-help and clinical care by prioritizing safety, usability, and real-time insights.
With the design philosophies guiding the structure of the questionnaires, I turned my attention to understanding the competitive landscape. Evaluating existing mental health apps helped me identify key gaps and opportunities to ensure the TeleClinical Care module addressed unmet needs while providing unique value to both patients and clinicians.
Step 4: Personas
To ensure the TeleClinical Care module was both innovative and effective, I explored leading mental health apps: Moodfit, Mentemia, MoodMission, and Sanvello. This analysis revealed their strengths and weaknesses, allowing me to identify critical gaps that TeleClinical Care could fill to stand out in the market.
Person: Brock
Person: Dr. Lauren


To better understand how the app could address the needs of both clinicians and patients, I mapped their thoughts, emotions, and pain points in detail
.png)
.png)
Building on these insights, I outlined the user journey to visualize how each persona interacts with the app from discovery to consistent use
.png)
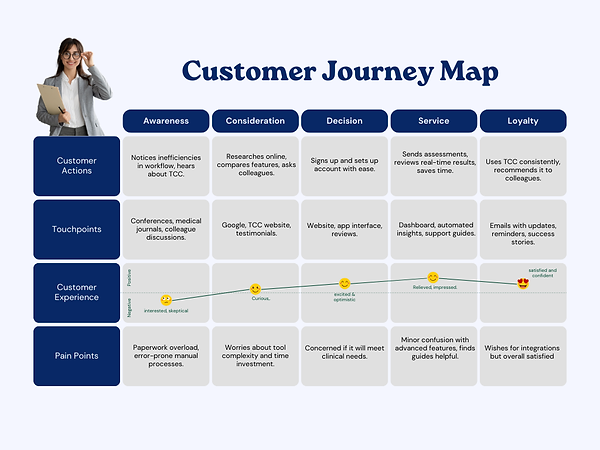.png)
Key Insights:
-
Bite-sized interfaces reduce cognitive load for patients.
-
Clinicians value exportable data and easy-to-read visualizations.
Building on the gaps identified in competitor analysis, I developed detailed personas to represent the key stakeholders—clinicians and patients—ensuring the design addressed their unique needs and pain points
3. Design Process
1. Requirements Gathering
Through collaboration with clinicians at Mindgardens Institute, functional and non-functional requirements were identified for two primary interfaces:
Questionnaire Interface:

Clinician Feedback Interface:

The TeleClinical Care module came to life through an iterative and research-driven design process. Each step focused on balancing clinical needs with user-centric design:
-
Requirements Gathering: Defined functional and non-functional requirements for the Questionnaire and Clinical Feedback Interfaces in collaboration with clinicians.
-
Low-Fidelity Prototyping and Testing: Created initial prototypes to visualize workflows and core interactions. Furthermore, I conducted testing sessions with clinicians and patient representatives, refining based on their insights.
-
High-Fidelity Design: Finalized accessible and visually engaging designs.
-
Implementation and Testing: Developed the module within the live app and performed extensive usability and E2E testing.
From
Research to Design
2. Low Fidelity Prototyping & Testing
Once the paper sketches felt solid, I moved them into Figma to create the low-fidelity prototype. This phase was all about structure and functionality—getting the user flow right before diving into aesthetics. Here’s what the low-fi prototype focused on:
-
Designed prototypes in color to capture key workflows early.
-
Focused on single-question screens, progress tracking, and accessible navigation.
Questionnaire Interface:
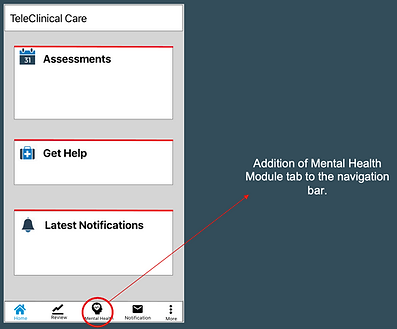

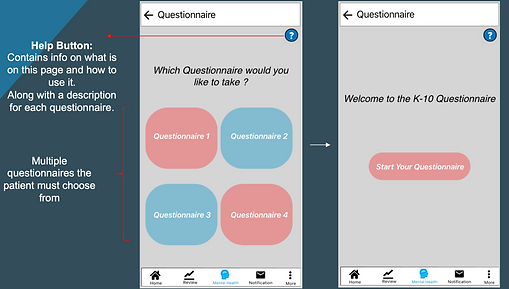



Clinician Feedback Interface:


Testing and Feedback
Once the low-fidelity prototype was ready, I presented it to key stakeholders for a quick round of testing and an initial design review. This step was crucial in refining the core features and overall design of the mental health module. After testing, I carefully analyzed their feedback alongside patient insights gathered by the clinicians, ensuring every update aligned with real user needs.
Iterations based on feedback:
-
Refined Color Palette: Aligned the design with the TCC app’s branding for a cohesive and professional look.
-
Enhanced Navigation: Added tabs and help icons to make switching between sections intuitive and user-friendly.
-
Improved Visuals: Introduced progress bars and simplified summaries to enhance clarity and engagement.
-
Emergency Support Visibility: Made emergency resources prominently accessible post-assessment to ensure user safety.
-
Feedback Clarity: Streamlined the clinician feedback interface with visual score indicators and explanatory notes for better understanding.
4. High Fidelity Prototype
With feedback incorporated, the prototypes evolved into high-fidelity designs—polished, engaging, and clinically aligned. Every element, from calming color palettes to accessibility features, was shaped to provide a seamless user experience for both patients and clinicians

All the feedback provided by the key stakeholders was incorporated into the High fidelity prototype. Below is a before -> after view of what the re-design looked like:
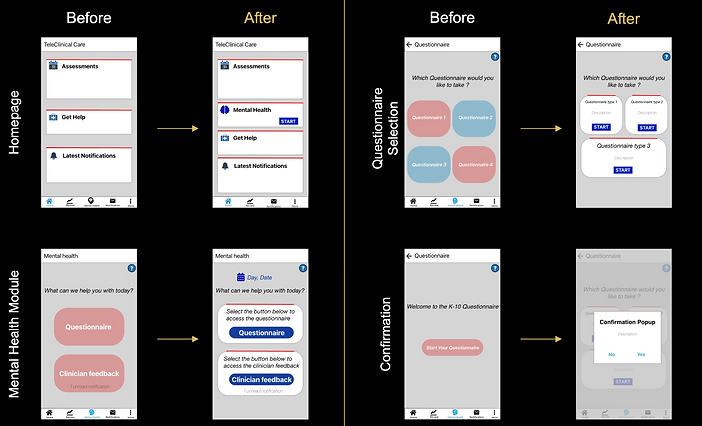
Hi-Fi Prototype – At a Glance
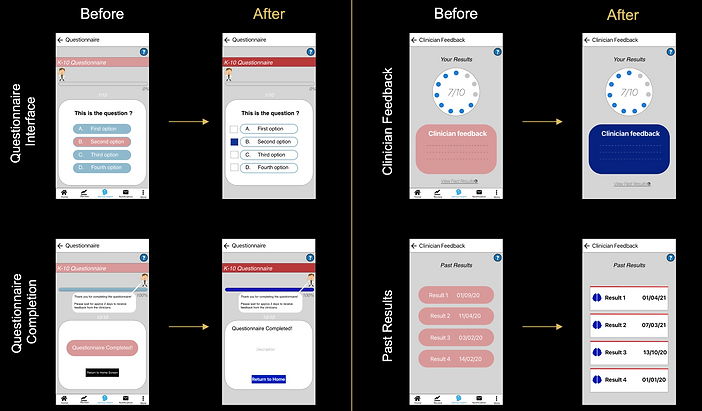
The polished high-fidelity prototype not only addressed user feedback but also adhered to clinical standards, ensuring a seamless, user-friendly experience. With this design finalized, the next step was to bring the vision to life through development and rigorous testing
4. Final Design
Introduction
The final design brought together all the insights, iterations, and testing to create a polished, user-friendly solution. With a focus on accessibility, clinical precision, and seamless integration, the mental health module was ready to meet the needs of both patients and clinicians in real-world use.
Implementation
The high-fidelity prototype was brought to life within the live TeleClinical Care app using React Native, ensuring compatibility with the existing framework. The development process adhered to the functional and non-functional requirements, resulting in a module that was intuitive for patients and efficient for clinicians. The mental health module was fully integrated into the app, enabling real-world use and testing.
Key Steps:
Questionnaire Interface: Developed interactive, single-question screens with progress tracking, help icons, and emergency resources.
Clinical Feedback Interface: Created dashboards for real-time insights, past results, and explanatory score breakdowns for patients and clinicians.
Integration: Ensured smooth compatibility with the TCC app, optimizing for fast loading times and usability.
Stakeholder Collaboration: Iteratively refined the module based on clinician and stakeholder feedback.
With the module implemented, it was time to showcase the final product—an intuitive, user-centered mental health solution that redefined digital assessments.
5. Testing
Introduction
Once the final design was implemented, comprehensive testing was conducted to ensure the mental health module met both user and clinical requirements. This process included functional testing to validate the technical aspects and usability testing to refine the user experience.
Functional Testing
Functional testing ensured the system worked seamlessly across all components. The following checks were performed:
-
Verified smooth and valid navigation between screens.
-
Confirmed workflows (e.g., accessing and completing questionnaires) were functioning as intended.
-
Conducted negative testing with invalid inputs to ensure robust error handling.
-
Ensured outputs met functional and non-functional requirements.
-
Tested for stability, ensuring no crashes or unexpected redirects occurred.
Usability Testing
Usability testing focused on evaluating user satisfaction and identifying areas for improvement. The Think Aloud Protocol was used to capture participant thoughts in real-time.
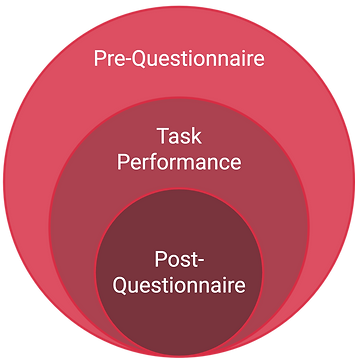
Usability Testing Procedure:
.png)
Pre-Questionnaire:
Participants shared their comfort level and prior experience with mobile applications. Since all participants were university students familiar with mobile apps, this step confirmed their readiness to engage with the testing tasks.
Task Performance:
Participants were asked to perform the following tasks:
-
Access the mental health module from the dashboard.
-
View available questionnaires and select one to complete (PHQ-9, GAD-7, or Daily Mood Chart).
-
Complete all three questionnaires from start to finish.
-
Navigate to the clinician feedback page, view numerical results, and access past records.
Post-Questionnaire:
After completing tasks, participants reflected on their overall experience. They provided feedback on what they liked, what they found challenging, and suggestions for further improvement.
Key Results & Insights:
1. Task Completion: 90% success rate across all key tasks, demonstrating the module's usability.
2. Positive Feedback: Participants appreciated the clean interface and straightforward navigation.
3. Improvements Identified: Suggestions included adding clearer instructions for first-time users and minor UI adjustments for readability.
6. Reflection
Working on the TeleClinical Care mental health module was one of the most meaningful experiences of my career. It wasn’t just about designing an app—it was about creating something that could genuinely make a difference in people's lives. Collaborating with clinicians, gathering patient insights, and iterating on every detail taught me the value of empathy, teamwork, and staying adaptable. Seeing the final module come together—empowering patients with accessible, easy-to-understand tools and helping clinicians streamline their workflows—was an incredibly fulfilling moment. It reinforced my belief that great design isn’t just functional; it’s impactful.
Next Steps
Planting the Seeds for Future Growth of
TCC - Mental Health
.png)
-
Real-World Testing: The next step is to see the module working in a in clinical settings. Gathering real-world feedback will be key to refining the design further and ensuring it delivers value to both patients and clinicians.
-
Feature Expansion: I’d love to build on the foundation by adding more tools like group therapy assessments or tracking long-term mental health trends; to address even more user needs.
-
AI-Powered Insights: There’s so much potential in leveraging AI to make feedback smarter and more personalized, giving clinicians deeper insights and patients a more tailored experience.
-
Accessibility Enhancements: Expanding accessibility features, like multilingual support and voice navigation, would help make the module truly inclusive and usable for a diverse range of users.
Thanks for checking out TeleClinical Care—where paper questionnaires got their long-overdue digital makeover!

